Hello, I’m Dr. Lin Shih-Chieh. Today, I’d like to introduce you to seborrheic dermatitis, a common chronic skin condition. It mainly affects the scalp, face, and other oily areas of the body, often causing dry, itchy skin, redness, and flaking, which can impact daily life and mental well-being. The condition results from factors like excess oil production, fungal growth, and immune response irregularities. Proper hygiene, medication, and lifestyle adjustments are key to managing the symptoms. This article will cover the causes, symptoms, and diverse treatment options for seborrheic dermatitis, helping patients manage it effectively and improve their quality of life.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic, recurring inflammatory skin condition primarily affecting the scalp, face, and other areas with active sebaceous glands. It often presents as dry, itchy skin, potentially affecting patients’ quality of life. Let’s explore its causes, symptoms, and effective treatments, along with daily management tips.
1. Causes of Seborrheic Dermatitis
- Excess Oil Production: Overactive sebaceous glands create a breeding ground for skin fungi (e.g., Malassezia).
- Fungal Overgrowth: Growth of Malassezia can trigger immune reactions, leading to inflammation and flaking.
- Immune System Issues: Weakened or compromised immunity (e.g., in diabetes or HIV patients) can increase susceptibility.
- Environmental and Lifestyle Factors: Temperature changes, stress, and irregular routines can worsen symptoms.
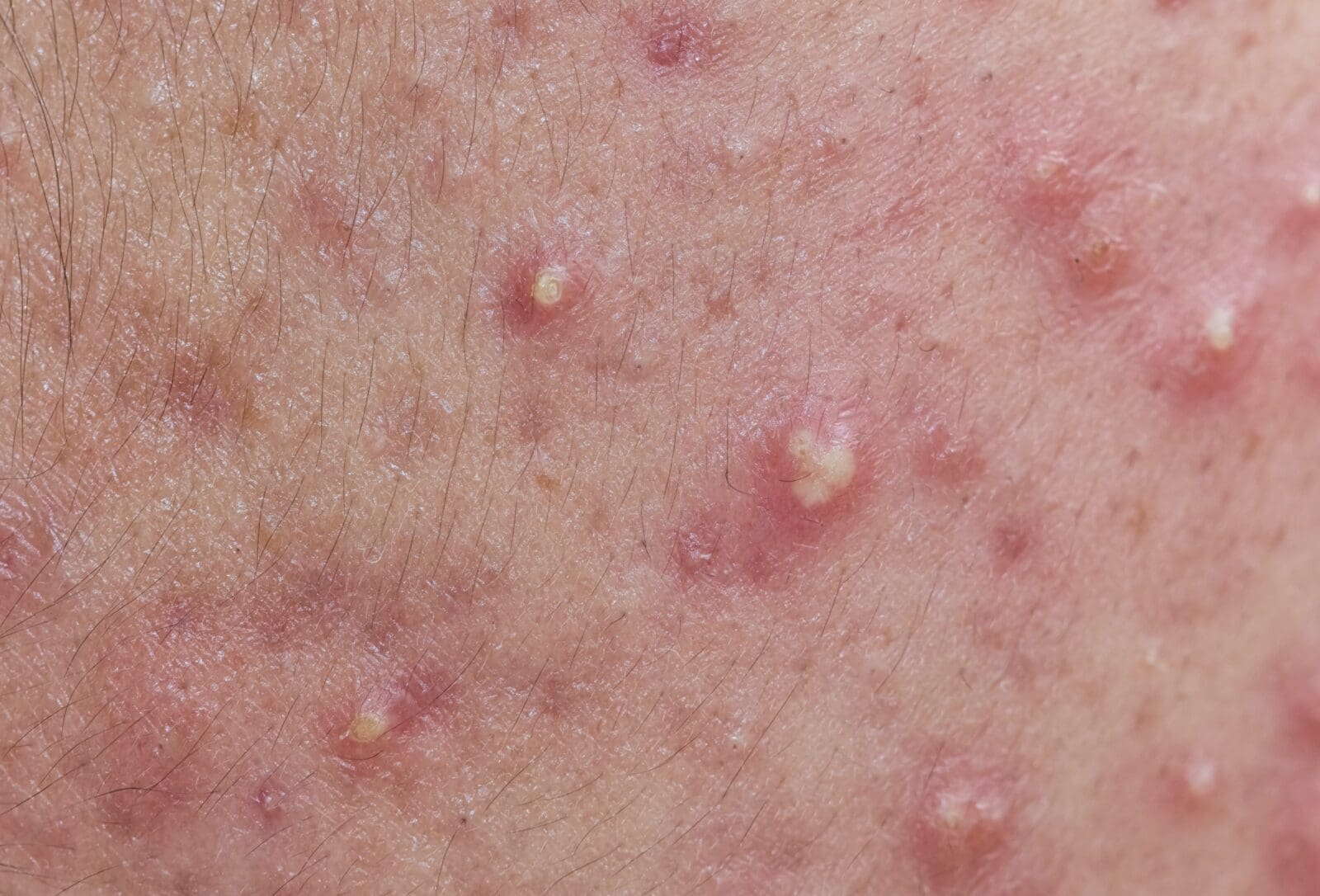
2. Common Symptoms
- Dry, Itchy Skin: Dryness, flaking, and intense itchiness, affecting the scalp, nose, eyebrows, behind the ears, or chest.
- Redness and Inflammation: Red patches or mild swelling on the skin.
- Dandruff: Increased flaking on the scalp, sometimes with a greasy feel.
- Sensitive Skin: Affected areas may react to climate changes or skincare products, causing more dryness or redness.
3. Treatment and Management
- Medication
- Antifungal Agents: Ketoconazole shampoo or Ciclopirox cream can reduce fungal growth, inflammation, and flaking.
- Topical Steroids: Short-term use of low-dose steroids (e.g., hydrocortisone) helps reduce redness and itching.
- Daily Care
- Gentle Cleansing: Use mild, soap-free cleansers to avoid excessive drying.
- Scalp Care: Use selenium sulfide or ketoconazole shampoos 2-3 times weekly to control dandruff.
- Moisturizing: Apply fragrance-free, low-irritant moisturizers daily to reduce dryness and itching.
- Diet and Lifestyle Adjustments
- Balanced Diet: Include foods rich in Omega-3 fatty acids (e.g., fish, nuts, flaxseed) to help reduce skin inflammation.
- Stress Reduction: Practice relaxation techniques like exercise or meditation to prevent flare-ups.
- Regular Sleep: Maintain a healthy sleep routine to support immune function.
- Environmental Control
- Avoid Triggers: Be aware of skincare or cosmetic products that may cause irritation.
- Humidity Management: Keep indoor humidity levels moderate to reduce skin dryness.
4. Long-Term Management
- Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic condition prone to recurrence, requiring ongoing care. Regular use of antifungal shampoos and creams, combined with lifestyle adjustments, is essential. If symptoms worsen or do not improve with treatment, consult a specialist for further evaluation.
5. When to See a Doctor
- If symptoms are severe, recurrent, or affecting your quality of life, consult a doctor.
- If you notice pustules or expanding redness, there may be a secondary infection that needs immediate treatment.
While seborrheic dermatitis and itchy skin can be challenging to manage, proper treatment and lifestyle adjustments can help control the symptoms and minimize the impact on daily life. If you have concerns or need personalized advice, consult with a dermatologist or family medicine physician for a tailored treatment plan.